February 11, 2025
Health In Sight: February 2025
Developments to watch for in healthcare this year

Artificial Intelligence — whether you’re converted, concerned, conflicted or all of the above, there will be no avoiding it this year. All the technology pundits and prognosticators say 2025 will be the year A.I. technology takes root in healthcare and everywhere.
Part of the push to introduce A.I. and other machine learning tech comes from the need to do more with less. Many governments have empty coffers, having spent big to save as many lives as possible during the coronavirus pandemic years. As treasurers resort to budgetary belt tightening, public hospitals are feeling the squeeze.
The pandemic continues to affect global production and supply chains, too. There’s less stuff available and it costs more. Vital medicines and hospital supplies are among the items difficult to access. Workforce shortages are ongoing.
The cost crunch is also hitting consumers and there are daily reminders that hip pocket pain is a key driver of election results. Apart from toppling governments, cost of living pressures has led to people either abandoning private health insurance or cutting back their cover. The domino effect here is putting private hospitals at risk. The 2024 Australian Private Hospitals Association conference was warned of imminent hospital closures, with private maternity hospitals potentially facing extinction.
While the financial headwinds swirl, populations are aging, driving up demand for healthcare, and increasing wait times and costs. So, it’s little wonder healthcare is looking to smart technology to save the day.
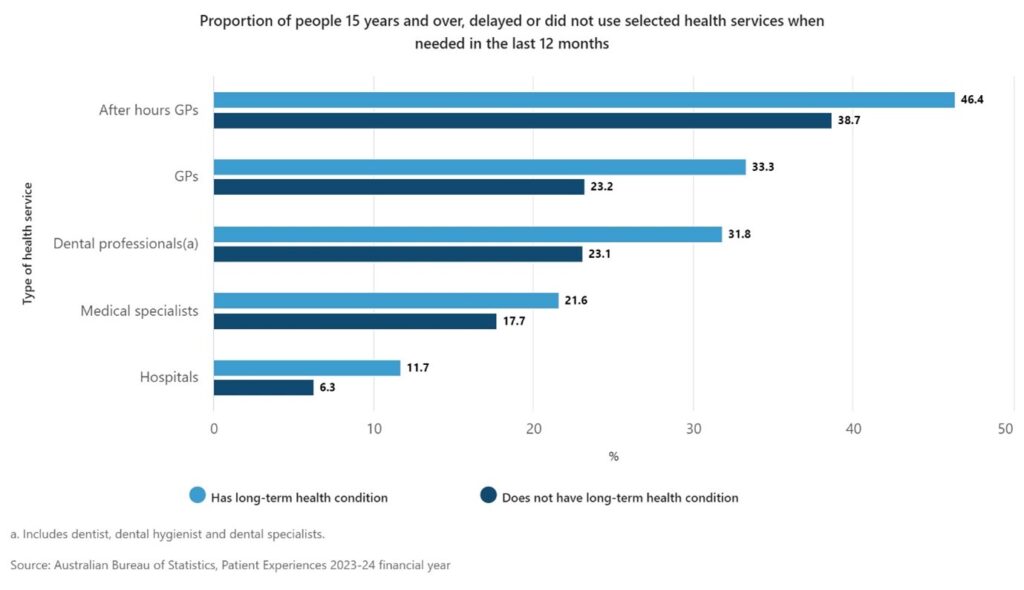
While the overall proportion of people surveyed who delayed or did not use health services when needed fell over the past year, this did not apply for people with long term health conditions, or people living in areas of most socio-economic disadvantage, who were more likely to forgo care.
Here are other factors likely to impact healthcare in 2025.
1. America the brave
The return of President Trump has global repercussions for healthcare. Halting foreign aid funding – temporarily or otherwise – has already resulted in a shortage of HIV medications in third world countries. President Trump has repealed legislation making medications cheaper for Americans, withdrawn the USA from the World Health Organization, and appointed a man with anti-vaccination (but pro-A.I.) views to lead the Department of Health and Human Services. Change is coming.
Significant gender gaps on service usage suggests Australian men do not prioritise their health, with women more likely to present at all the healthcare services listed in the survey. For example, 87.3% of women saw a GP in 2023-24, compared to 77.7% of men. Use of telehealth fell, with the data revealing women are significantly more likely to use telehealth services than men.
To read more of the Patient Experience survey results, go to Patient Experiences, 2023-24 financial year | Australian Bureau of Statistics.
2. A.I everywhere
President Trump has removed restrictions that he and his advisors perceived to be hindering rapid development of A.I. technology. Despite many calling for safety and ethical guardrails on machine learning tech, it looks like it’s full steam ahead in the USA. In healthcare, the enterprise medical records systems could be under threat from A.I-powered assistants and countless new use cases for A.I. pop up daily. A few that caught our eye recently include:
- cameras over hospital beds to trigger falls risks warning and calculate risk of bed sores,
- patient-worn A.I.-powered sensors that take observations and supplement staffing in a hospital ward making do with fewer nurses, and
- A.I. algorithms to detect patients who are likely to be frequent fliers at Emergency Departments and trigger intervention prevention programs.
A.I. diagnostic tools are delivering increasingly accurate data in trials, but there’s justified caution about letting the machines serve as primary decision makers.
The United Kingdom’s National Health Service (NHS) is also committing to AI technology, introducing a tech bundle called Humphrey after the character from Yes Minister, to increase NHS productivity, and make it easier for consumers to find and book appointments. Judging by the resources linked below, this approach will typify AI adoption in 2025 – deployment to reduce the administrative burden of repetitive tasks, reporting and, potentially, clinical coding. The catchphrase, “let doctors be doctors” is echoing through the halls of healthcare and resonating with time-poor clinicians complaining they spend more time on paperwork than patient care.
This project is an example of focusing on opportunities to improve health equity, rather than just outcomes data. Cleveland’s Metro Health Institute for Hope recently posted on this issue, suggesting that asking communities how to change health outcomes may be more effective than monitoring distressing data. More detail on the Institute’s logic can be found here: Why health equity’s goal shouldn’t be outcomes
3. Virtually everywhere
The cost of keeping patients in hospital and aged care beds beds is rising so insurers, governments and healthcare companies are looking more closely at the price to keep patients in their own homes. Virtual care in the home, supported by virtual and mobile nurses, telehealth advisors and health coaches, (or South Korea’s A.I.-powered robot grandchild) is not a new concept. But the tide seems to have shifted, partly due to the competitive pricing of scalable, interoperable cloud technology supporting real time data exchange. Safe virtual care depends on finding the right patient, home and carer combinations, and the on-call ability to respond quickly to changes in health status – or patient anxiety levels. Scalability and success of this model of care will hinge on whether governments and funders can find cost-effective funding models that adequately compensate clinicians for their work.
4. Bad actors
An increasingly digitised healthcare world attracts cyber-criminals like flies to a barbecue. Hospitals are increasingly seen as soft targets; its estimated ransomware attacks have cost US hospitals $21.9 billion in downtime since 2018. There’s also concern the introduction of A.I. systems may provide a wormhole for the crooks to tunnel through. Just as hospitals must consider ‘interactions’ between medications, they now have to look into how all their information technology systems interact and counteract cybercrime.
5. Consumer data
Like virtual care, wearable health monitoring technology isn’t a new idea, but it is getting smaller, smarter and less intrusive. Watches and rings now offer real time insights into stress levels, oxygen saturation, pain scores, sleep patterns, menstrual cycles, infection risks, and much more. With all this extra data available, the unwell and worried well will want it to be actionable and shareable with their health teams. Health records systems with true connectivity are increasingly important.
6. Healthcare as a community
Greater connectivity of data – enabling predictive research from aggregated, anonymous ‘data lakes’, is increasingly realistic in 2025. But secure sharing of data requires co-operation and collaboration between humans. Software and technology vendors, government procurement teams and healthcare businesses can no longer keep their heads in the sand when it comes to adopting industry data standards and thereby future-proofing interoperability. The CSIRO-led Sparked community in Australia is an excellent example of getting this right.
Community health is holistic – social issues such as homelessness, addictions, health literacy, family and domestic violence, and access to mental health care, all impact our primary and tertiary care systems. Being able to share timely information that enables earlier interventions and more appropriate care from multidisciplinary healthcare teams, is ever more important in an ecosystem of tight budgets and time poor clinicians.
Can technology save the day? We’ll leave the last word with the CEO of the ever-innovative Mayo Clinic, who spoke at the World Economic Forum in Davos. Doctor Gianrico Farrugia is reported as saying the following:
“I personally would not want to have my healthcare, in some specialties, without A.I. because I firmly believe I will get a better outcome… Shame on all of us, shame on government, if we cannot, at this moment in time, come together and create the pathways and the architecture to be able to do what we already know we can do: provide better outcomes for patients at a scale that was unimaginable a few years ago.”
At MediRecords, we believe technology should empower healthcare professionals. That’s why we’re building AI-powered platform capabilities designed to optimise workflows, reduce administrative burdens, and make critical patient information more accessible. Contact our Sales Team to learn more about our expanding suite of AI features.
References
The US Halt In Foreign Aid ‘Could Mean Life Or Death For Millions’
How the US foreign aid freeze is intensifying humanitarian crises across the globe | CNN
https://www.mobihealthnews.com/news/elon-musk-confirms-trump-agrees-shut-down-usaid
Reevaluating And Realigning United States Foreign Aid – The White House
President Trump orders US to exit World Health Organization
Health insurance: a horror week bodes ill | Health Services Daily
Healthscope teeters one step closer to the brink | Health Services Daily
UCSD explores AI cameras for hospital rooms
Sibel Health to provide wireless monitoring to hospitals in Denmark | MobiHealthNews
NHS using AI to predict frequent emergency service users
Why Classic EMR Vendors Will Be Replaced by openEHR and AI Agents Architectures
Providence CEO ‘totally blown away’ by OpenAI’s healthcare work
Reducing clinicians’ administrative tasks with artificial intelligence | MobiHealthNews
https://www.beckershospitalreview.com/ai/whats-next-for-healthcare-ai-in-2025.html
‘Humphrey’ AI tool launched to streamline NHS and public services
AI Scribing in Healthcare: Why Some Hospitals Are Pulling Ahead
Driving momentum in healthcare technology amid dramatic change | Wolters Kluwer
Executives forecast AI’s place in healthcare in 2025, part one | MobiHealthNews
Executives forecast AI’s place in healthcare in 2025, part two | MobiHealthNews
How Kaiser Permanente quadrupled its advanced-care-at-home program
Could virtual hospitals be the solution to the broken NHS? | Digital Health
AI care robot doll from Korea eyes US entry in 2025 | MobiHealthNews
No Going Home. Hospital at Home is a Hype Machine
https://www.healthcareitnews.com/news/what-will-ai-do-telemedicine-2025-more-you-might-think
The dark side of AI for hospitals
Ransomware attacks cost healthcare $21.9B in downtime
Two new smart rings unveiled at CES | MobiHealthNews
QALO unveils new silicon smart ring | MobiHealthNews
2024 predictions: Health tech suppliers on what’s in store
7 Healthcare Trends That Will Transform Medicine In 2025
8 must-have digital technologies for health systems in ’25
‘Shame on all of us’ if we can’t get healthcare AI right: Mayo Clinic CEO